 |
Open CASCADE Technology
7.4.0
|
|
 |
Open CASCADE Technology
7.4.0
|
|

Welcome to Open CASCADE Technology (OCCT), a software development platform providing services for 3D surface and solid modeling, CAD data exchange, and visualization. Most of OCCT functionality is available in the form of C++ libraries. OCCT can be best applied in development of software dealing with 3D modeling (CAD), manufacturing / measuring (CAM) or numerical simulation (CAE).
Open CASCADE Technology and all materials, including this documentation, is Copyright (c) 1999-2019 by OPEN CASCADE S.A.S. All rights reserved.

Open CASCADE Technology is free software; you can redistribute it and / or modify it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public License (LGPL) version 2.1, with additional exception.
Note that LGPL imposes some obligations on the application linked with Open CASCADE Technology. If you wish to use OCCT in a proprietary application, please pay a special attention to address the requirements of LGPL section 6. At minimum the following should be considered:
If you want to use Open CASCADE Technology without being bound by LGPL requirements, please contact Open CASCADE company for a commercial license.
Note that Open CASCADE Technology is provided on an "AS IS" basis, WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND. The entire risk related to any use of the OCCT code and materials is on you. See the license text for formal disclaimer.
You are hereby informed that all software is a property of its respective authors and is protected by international and domestic laws on intellectual property and trademarks. Should you need further information, directly contact the authors.
CAS.CADE and Open CASCADE are registered trademarks of OPEN CASCADE S.A.S.
Linux is a registered trademark of Linus Torvalds.
Windows is a registered trademark of Microsoft Corporation in the United States and other countries.
Mac and the Mac logo are trademarks of Apple Inc., registered in the U.S. and other countries.
The following parties are acknowledged for producing tools which are used within Open CASCADE Technology libraries or for release preparation.
You are hereby informed that all rights to the software listed below belong to its respective authors and such software may not be freely available and/or be free of charge for any kind of use or purpose. We strongly recommend that you carefully read the license of these products and, in case you need any further information, directly contact their authors.
Qt is a cross-platform application framework that is widely used for developing application software with graphical user interface (GUI). Qt is free and open source software distributed under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public License. In OCCT Qt is used for programming samples. If you need further information on Qt, refer to Qt Homepage (https://www.qt.io/)
Tcl is a high-level programming language. Tk is a graphical user interface (GUI) toolkit, with buttons, menus, listboxes, scrollbars, and so on. Taken together Tcl and Tk provide a solution to develop cross-platform graphical user interfaces with a native look and feel. Tcl/Tk is under copyright by Scriptics Corp., Sun Microsystems, and other companies. However, Tcl/Tk is an open source, and the copyright allows you to use, modify, and redistribute Tcl/Tk for any purpose, without an explicit license agreement and without paying any license fees or royalties. To use Tcl/Tk, refer to the Licensing Terms (https://www.tcl.tk/software/tcltk/license.html).
FreeType 2 is developed by Antoine Leca, David Turner, Werner Lemberg and others. It is a software font engine that is designed to be small, efficient, highly customizable and portable while capable of producing high-quality output (glyph images). This product can be used in graphic libraries, display servers, font conversion tools, text image generation tools, and many other products. FreeType 2 is released under two open-source licenses: BSD-like FreeType License and the GPL (https://www.freetype.org/license.html).
Intel(R) Threading Building Blocks (TBB) offers a rich and complete approach to expressing parallelism in a C++ program. It is a library that helps you to take advantage of multi-core processor performance without having to be a threading expert. Threading Building Blocks is not just a threads-replacement library. It represents a higher-level, task-based parallelism that abstracts platform details and threading mechanisms for scalability and performance. TBB version 2017 is available under Apache 2.0 license, while older versions until 4.4 are available under GPLv2 license with the runtime exception (https://www.threadingbuildingblocks.org).
OpenGL is an industry standard API for 3D graphics used by OCCT for implementation of 3D viewer. OpenGL specification is developed by the Khronos group, https://www.khronos.org/opengl/. OCCT code includes header file glext.h obtained from Khronos web site.
VTK – The Visualization Toolkit (VTK) is an open-source, freely available software system for 3D computer graphics, image processing and visualization. OCCT VIS component provides adaptation functionality for visualization of OCCT topological shapes by means of VTK library. If you need further information on VTK, refer to VTK Homepage https://www.vtk.org/.
Doxygen developed by Dimitri van Heesch is open source documentation system for C++, C, Java, Objective-C, Python, IDL, PHP and C#. This product is used in Open CASCADE Technology for automatic creation of Technical Documentation from C++ header files. If you need further information on Doxygen, refer to https://www.stack.nl/~dimitri/doxygen/index.html.
Graphviz is open source graph visualization software developed by John Ellson, Emden Gansner, Yifan Hu and Arif Bilgin. Graph visualization is representiation of structured information as diagrams of abstract graphs and networks. This product is used together with Doxygen in Open CASCADE Technology for automatic creation of Technical Documentation (generation of dependency graphs). Current versions of Graphviz are licensed on an open source basis under The Eclipse Public License (EPL) (https://www.graphviz.org/license/).
Inno Setup is a free script-driven installation system created in CodeGear Delphi by Jordan Russell. In OCCT Inno Setup is used to create Installation Wizard on Windows. It is licensed under Inno Setup License (http://www.jrsoftware.org/files/is/license.txt).
FreeImage is an Open Source library supporting popular graphics image formats, such as PNG, BMP, JPEG, TIFF, and others used by multimedia applications. This library is developed by Hervé Drolon and Floris van den Berg. FreeImage is easy to use, fast, multithreading safe, compatible with all 32-bit or 64-bit versions of Windows, and cross-platform (works both with Linux and Mac OS X). FreeImage is optionally used by OCCT to work with images, on conditions of the FreeImage Public License (FIPL) (https://freeimage.sourceforge.net/freeimage-license.txt).
David M. Gay's floating point routines (dtoa.c) are used for fast reading of floating point values from text strings. These routines are available under MIT-like license (see https://www.netlib.org/fp/).
CMake is an open-source, cross-platform family of tools designed to build, test and package software. CMake is used to control the software compilation process using simple platform and compiler independent configuration files, and generate native makefiles and workspaces that can be used in the compiler environment of your choice. OCCT uses CMake as a build system. CMake is available under BSD 3-Clause license. See more at https://cmake.org/
Cotire (compile time reducer) is a CMake module that speeds up the build process of CMake based build systems by fully automating techniques as precompiled header usage and single compilation unit builds for C and C++. Cotire is included in OCCT repository and used optionally by OCCT CMake scripts to accelerate builds by use of precompiled headers. Cotire is licensed under the MIT license (https://github.com/sakra/cotire/blob/master/license).
FFmpeg is an Open Source framework supporting various image, video and audio codecs. FFmpeg is optionally used by OCCT for video recording, on LGPL conditions (https://www.ffmpeg.org/legal.html).
MikTEX is up-to-date implementation of TeX/LaTeX and related programs for Windows. It is used for generation of User and Developer Guides in PDF format. See https://miktex.org for information on this tool.
RapidJSON is an Open Source JSON parser and generator for C++. RapidJSON is optionally used by OCCT for reading glTF files (https://rapidjson.org/).
Adobe Systems, Inc. provides Adobe Reader, which can be used to view files in Portable Document Format (PDF).
OCCT documentation is provided in several forms:
See OCCT Documentation Guide for details on OCCT documentation system.
Generation of HTML documentation
To generate HTML documentation from sources contained in dox subdirectory, you need to have Tcl and Doxygen 1.8.5 (or above) installed on your system.
Use script gendoc (batch file on Windows, shell script on Linux / Mac OSX) to generate documentation.
To generate Overview documentation:
cmd> gendoc -overview
To generate Reference manual:
cmd> gendoc -refman
Run this command without arguments to get help on supported options.
Open CASCADE Technology is designed to be highly portable and is known to work on wide range of platforms. Current version is officially certified on Windows (IA-32 and x86-64), Linux (x86-64), OS X / macOS (x86-64), Android (armv7 and x86), and iOS (armv7, arm64) platforms.
The tables below describe the recommended software configurations for which OCCT is certified to work.
| OS | Compiler |
|---|---|
| Windows | Microsoft Visual Studio: 2008 SP1, 2010 SP1, 2012 Update 4, 2013 Update 5, 2015 Update 3, 2017 1, 2019 GCC 4.3+ (Mingw-w64) |
| Linux | GNU gcc 4.3+ LLVM CLang 3.6+ |
| OS X / macOS | XCode 6 or newer |
| Android | NDK r10, GNU gcc 4.8 or newer |
1) VC++ 141 64-bit is used for regular testing and for building binary package of official release of OCCT on Windows.
| Component | Requirement |
|---|---|
| Graphic library | OpenGL 3.3+, OpenGL ES 2.0+ Direct3D 9 |
| Qt (for samples and demos) | Desktop: Qt 4.8.6+ https://www.qt.io/download/ Android: Qt 5.3.2+ https://www.qt.io/download/ |
| TCL (for testing tools) | Tcl/Tk 8.6.3+ https://www.tcl.tk/software/tcltk/download.html or ActiveTcl 8.6 https://www.activestate.com/activetcl/downloads (for Windows) |
| Freetype (for text rendering) | FreeType 2.4.11-2.7.1 https://sourceforge.net/projects/freetype/files/ |
| FreeImage (optional, for support of common 2D graphic formats) | FreeImage 3.17.0+ https://sourceforge.net/projects/freeimage/files |
| FFmpeg (optional, for video recording) | FFmpeg 3.1+ https://www.ffmpeg.org/download.html |
| RapidJSON (optional, for reading glTF) | RapidJSON 1.1+ https://rapidjson.org/ |
| Intel TBB (optional, for multithreaded algorithms) | TBB 4.x or 5.x https://www.threadingbuildingblocks.org/ |
| VTK (for VTK Integration Services | VTK 6.1+ https://www.vtk.org/download/ |
| Doxygen (optional for building documentation) | Doxygen 1.8.5+ https://www.stack.nl/~dimitri/doxygen/download.html |
| Component | Requirement |
|---|---|
| Minimum memory | 512 MB, 1 GB recommended |
| Free disk space (complete installation) | 600 MB approx. |
On desktop, 3D viewer for optimal performance requires graphics processing unit (GPU) supporting OpenGL 3.3 or above. Ray tracing requires OpenGL 4.0+ or OpenGL 3.3+ with GL_ARB_texture_buffer_object_rgb32 extension. Textures within ray tracing will be available only when GL_ARB_bindless_texture extension is provided by driver.
On mobile platforms, OpenGL ES 2.0+ is required for 3D viewer (OpenGL ES 3.1+ is recommended). The ray tracing is not yet available on mobile platforms. Some old hardware might be unable to execute complex GLSL programs (e.g. with high number of light sources, clipping planes).
OCCT 3D Viewer, in general, supports wide range of graphics hardware - from very old to new. Therefore, if you observe some unexpected visual issues - first check for OpenGL driver update (or firmware update in case of mobile platforms); but beware that driver update might also come with new bugs. Don't forget to report these bugs to vendors.
In most cases you need to rebuild OCCT on your platform (OS, compiler) before using it in your project, to ensure binary compatibility. See Building OCCT from sources for instructions on building OCCT from sources on supported platforms.
On Windows Open CASCADE Technology can be installed with binaries precompiled by Visual C++ 2010 with installation procedure.
Recommendation:
If you have a previous version of OCCT installed on your station, and you do not plan to use it along with the new version, you might want to uninstall the previous version (using Control Panel, Add/Remove Programs) before the installation of this new version, to avoid possible problems (conflict of system variables, paths, etc).
Attention: For full installation OCCT requires approximately 650 Mb of disk space, but during the installation process you will need 1,2 Gb of free disk space.
OCCT installation with reference documentation requires 1,4 Gb on disk.
The includes and binaries of third-party libraries necessary for building and launching OCCT are included into binary distribution (built with Visual C++ 2010). When the installation is complete, you will find the directories for 3rd party products (some might be absent in case of custom installation) and the main OCCT directory:
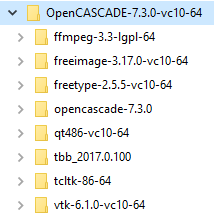
The contents of the OCCT-7.4.0 directory (called further "OCCT root", or $CASROOT) are as follows:
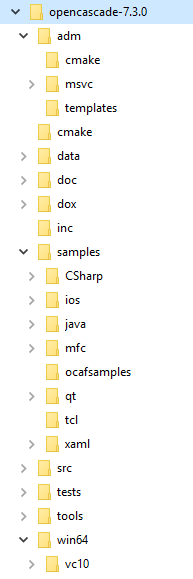
To run any Open CASCADE Technology application you need to set the environment variables.
You can define the environment variables with env.bat script located in the $CASROOT folder. This script accepts two arguments to be used: the version of Visual Studio (vc10 – vc142) and the architecture (win32 or win64).
The additional environment settings necessary for compiling OCCT libraries and samples by Microsoft Visual Studio can be set using script custom.bat located in the same folder. You might need to edit this script to correct the paths to third-party libraries if they are installed on your system in a non-default location.
Script msvc.bat can be used with the same arguments for immediate launch of Visual Studio for (re)compiling OCCT.
If OCCT was built by Code::Blocks, you can define the environment variables with env_cbp.sh or custom_cbp.sh script.
If OCCT was built by Automake, you can define the environment variables with env_amk.sh or custom_amk.sh script.
The scripts are located in the OCCT root folder.
Draw is a command interpreter based on TCL and a graphical system used for testing and demonstrating OCCT modeling libraries.
Draw can be used interactively to create, display and modify objects such as curves, surfaces and topological shapes.
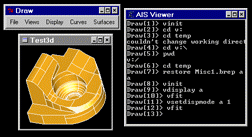
Scripts can be written to customize Draw and perform tests. New types of objects and new commands can be added using C++ programming language.
Draw contains:
You can add new custom test harness commands to Draw in order to test or demonstrate a new functionality, which you are developing.
Currently DRAW Test Harness is a single executable called DRAWEXE.
Commands grouped in toolkits can be loaded at run-time thereby implementing dynamically loaded plug-ins. Thus you can work only with the commands that suit your needs adding the commands dynamically without leaving the Test Harness session.
Declaration of available plug-ins is done through special resource file(s). The pload command loads the plug-in in accordance with the specified resource file and activates the commands implemented in the plug-in.
The whole process of using the plug-in mechanism as well as the instructions for extending Test Harness is described in the Draw Test Harness.
Draw Test Harness provides an environment for OCCT automated testing system. Check its Automated Testing System for details.
Remarks:
On Linux:
Draw[1]> prompt appears in the command window
Type pload ALL
On Windows:
Launch Draw executable from Open CASCADE Technology\Test Harness\Draw Test Harness item of the Start\Programs menu or Use $CASROOT\draw.bat file to launch DRAWEXE executable.
Draw[1]> prompt appears in the command window
Type pload ALL
Creating your first geometric objects
Manipulating the view
Running demonstration files
Getting Help
Visual C++ programming samples containing 10 Visual C++ projects illustrating how to use a particular module or functionality.
The list of MFC samples:
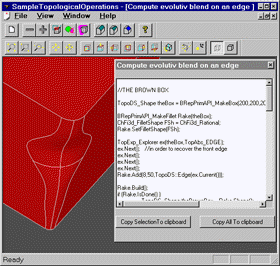
Remarks:
See Readme for details.
OCCT contains three samples based on Qt application framework
Import Export programming sample contains 3D Viewer and Import / Export functionality.
The Qt programming tutorial teaches how to use Open CASCADE Technology services to model a 3D object. The purpose of the tutorial is not to explain all OCCT classes but to help start thinking in terms of the Open CASCADE Technology.
This tutorial assumes that the user has experience in using and setting up C++. From the viewpoint of programming, Open CASCADE Technology is designed to enhance user's C++ tools with high performance modeling classes, methods and functions. The combination of these resources allows creating substantial applications.
See also: OCCT Tutorial
Remarks:
C# sample demonstrates integration of OCCT 3D Viewer and Import / Export functionality into .NET applications (using Windows Forms and WPF front ends).
Import:
Export:
See C# sample Readme for details.
There is also another C# example with the same functionality, which demonstrates the integration of Direct3D Viewer into .NET applications using WPF front end.
See Direct3D C# sample Readme for details.
There are two samples are representing usage OCCT framework on Android mobile platform. They represent an OCCT-based 3D-viewer with CAD import support in formats BREP, STEP and IGES: jniviewer (java) and AndroidQt (qt+qml)
jniviewer

Java – See Android Java sample Readme for details.
AndroidQt

Qt – See Android Qt sample Readme for details.
There is a sample demonstrating usage of OCCT on iOS with Apple UIKit framework.
See iOS sample Readme for details.